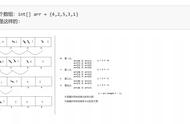
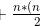我们定义了一个静态方法 bubbleSort() 来实现冒泡排序算法。
我们使用两个嵌套的 for 循环来遍历数组中的每个元素,并比较相邻的元素。如果它们的顺序不正确,我们就交换它们的位置。然后我们继续遍历数组,直到没有相邻的元素需要交换为止。最后,我们返回排好序的数组。
public class BubbleSort {
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
// 遍历数组中的每个元素
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ) {
// 在每次遍历中,最后 i 个元素已经排好序了
for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j ) {
// 如果相邻的元素比较大,则交换它们
if (arr[j] > arr[j 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j 1];
arr[j 1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5, 2, 7, 3, 9, 1, 6};
System.out.println("Before sorting:");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num " ");
}
System.out.println();
int[] sortedArr = bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.println("After sorting:");
for (int num : sortedArr) {
System.out.print(num " ");
}
}
}
在 main() 方法中,我们创建了一个数组并打印出排序前的数组。然后我们调用 bubbleSort() 方法对数组进行排序,并打印出排序后的数组。
,