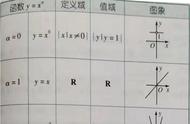
"""非线性回归"""
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from linear_regression import LinearRegression
data = pd.read_csv('../data/non-linear-regression-x-y.csv')
x = data['x'].values.reshape((data.shape[0], 1))
y = data['y'].values.reshape((data.shape[0], 1))
data.head(10)
# visualize the training and test datasets to see the shape of the data
plt.plot(x, y)
plt.show()
# Set up linear regression parameters.
num_iterations = 50000
learning_rate = 0.02
polynomial_degree = 15 # The degree of additional polynomial features.
sinusoid_degree = 15 # The degree of sinusoid parameter multipliers of additional features.
normalize_date = True
# Init linear regression instance.
# linear_regression = LinearRegression(x, y, normalize_date) # 线性回归
linear_regression = LinearRegression(x, y, polynomial_degree, sinusoid_degree, normalize_date)
# Train linear regression
(theta, cost_history) = linear_regression.train(
learning_rate,
num_iterations
)
print('开始损失: {:.2f}'.format(cost_history[0]))
print('结束损失: {:.2f}'.format(cost_history[-1]))
theta_table = pd.DataFrame({'Model Parameters': theta.flatten()})
# Plot gradient descent progress.
plt.plot(range(num_iterations), cost_history)
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Cost')
plt.title('Gradient Descent Progress')
plt.show()
# Get model predictions for the trainint set.
predictions_num = 1000
x_predictions = np.linspace(x.min(), x.max(), predictions_num).reshape(predictions_num,1)
y_predictions = linear_regression.predict(x_predictions)
# Plot training data with predictions.
plt.scatter(x, y, label='Training Dataset')
plt.plot(x_predictions, y_predictions, 'r', label='Prediction')
plt.show()
执行效果:
开始损失: 580629.11
结束损失: 8777.68

非线性回归方程: